What is the life cycle of plants?
Plants are living things, they grow and reproduce like any other living thing. They also follow a cyclical process in several stages, such as starting a new life, growing and then returning to the initial stage (reproducing). Plants start their life from seeds and grow into mature plants.
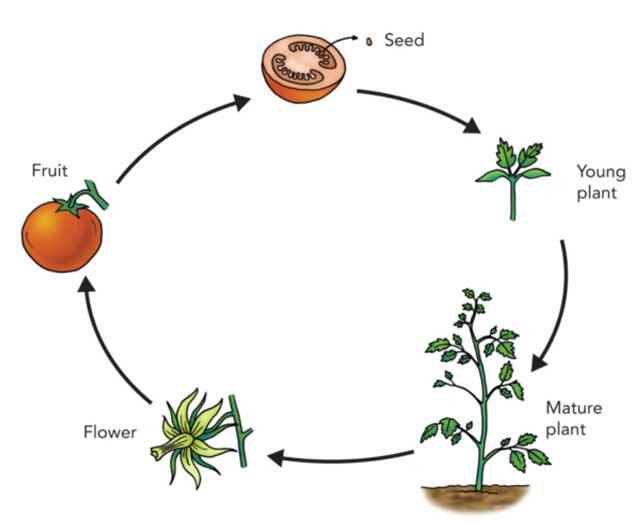
Stages of the plant life cycle
Most plants begin their life as seeds. These seeds are buried in the soil by various methods, where they germinate. After germination, the first leaves of the plants emerge, known as seedlings. After that, the further growth of the plants begins until they reach maturity. At this stage, the plants pollinate and produce seeds so that their species continues to survive by restarting the life cycle.
The life cycle of plants can be divided into 3, 4 and 5 stages, but the most accepted model is the 5-stage model.
- Seed
- Germination and seedling
- Growing to maturity
- Reproductive stage
- Seed dispersal
Seed – 1street Scenery
Seeds are the embryos of plants that contain the food necessary for their initial development. They are protected by a resistant outer layer until the right conditions for germination are met.
These seeds are dispersed across the land in many ways, including by moving water, wind, animals, and human activity. When the seeds reach a suitable environment with adequate moisture and temperature levels, they germinate and begin their life cycle.
Germination and seedling – 2North Dakota Scenery
After germination, the seed breaks through its outer layer and develops the first roots and leaves, known as cotyledons. Once the initial structures of the seed emerge from the soil, it is called a seedling.
At this stage, the roots begin to absorb water from the soil, while the leaves begin photosynthesis for food production. The seedling continues its development and forms plumules. These plumules are the first stems from which new leaves develop.
Growing into maturity – 3Third Scenery
Seedling growth continues until the plant reaches full maturity. The plant needs many things necessary for healthy growth, such as water, nutrient-rich soil, air, sunlight, proper temperature, and adequate space from other plants. (For more information, see How do plants grow?).
As plants mature, they develop stronger roots and a large number of branches and leaves. At this stage, they are ready to enter the reproductive stage to produce flowers and new seeds.
Reproductive stage – 4He Scenery
- Stamen (male parts): It produces the pollen (a powdery substance) necessary for the fertilization of the pistil.
- Pistil (female parts): Produces seeds after fertilization.
When pollen from the stamen reaches the pistil, fertilization occurs and seeds are produced in the process.
Seed dispersal – 5He Scenery
Once seeds are produced, plants must disperse them in favorable places where they can germinate and begin a new life cycle. There are several methods for seed dispersal:
- Wind: Strong gusts of wind blow seeds away from plants. Light, fibre-laden seeds also float through the air and reach distant places.
- Water: When plant seeds fall into the river, they are carried to distant places.
- Animals: Animals eat the fruits of plants that contain seeds and then excrete the seeds in different places.
Pollination methods
The pollination process in which pollen reaches the pistil from the stamen occurs through several methods:
- Insect pollination: Insects visit flowers to drink their sweet nectar. They move from flower to flower and unwittingly transfer pollen from the stamens to the pistils.
- Wind pollination: Many plants have male and female parts separated by a great distance. Wind plays a crucial role in transporting pollen from the stamen to the pistil during strong winds.
- Animal pollination: Animals, including birds and land animals, play a similar role to insects. They also visit plants in search of food and carry pollen that sticks to their bodies. They transfer pollen from the stamens to the pistils as they move between plants and their flowers.
What happens to plants without seeds?
Many plants do not produce flowers or seeds to reproduce, but instead grow from the spores of their parent plants. Spores can be parts of a plant or the remains of a dead plant. New plants are produced from the spores and continue to grow.
See Plants without flowers For more information.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is self-pollination and cross-pollination?
In self-pollination, pollen from the anther reaches the stigma of the same flower or a different flower of the same plant. However, cross-pollination is a little different. It occurs when pollen from the anther of one plant reaches the stigma of the flower of another plant of the same species. Both processes can occur naturally or artificially.
What is asexual reproduction in plants?
Plants that grow without fertilization are called asexually reproducing plants. Asexual reproduction can occur by fragmentation, spores, budding, and vegetative propagation. Potatoes are a famous example of asexual plant reproduction.
What is alternation of generations?
The life cycle of plants is divided into two main phases: haploid and diploid. These two phases of the plant life cycle can also alternate and this process is called alternation of generations.
Alternation of generations is the main type of life cycle in plants. In this life cycle, the haploid sexual phase (gametophytes), which consists of a single set of chromosomes, is converted into a diploid asexual phase (sporophytes), which contains two sets of chromosomes. Both haploids and diploids are multicellular and their cells divide by meiosis and mitosis, respectively. This alternation of generations is not only common in plants but is also found in algae and fungi.
Interesting facts
- The Great Basin pine is the oldest tree in the world, estimated to be 5,056 years old.
- Coco de Mer is the seed of a palm tree, can weigh around 18 Kg (40 lbs) and reach a height of 12 feet.
- Rose, jasmine and lily are the flowers with the strongest scent.
- When a seed does not germinate, it is in a dormant state. At this stage, it is nothing more than dead matter.