Chemical fertilizers play an important role in modern agriculture, influencing plant growth and crop yields. These fertilizers are intended to provide essential nutrients to plants and at the same time compensate for deficiencies in the soil composition. However, its widespread use has raised concerns about the effects on plant health, soil fertility, and environmental sustainability. This essay investigates the effects of chemical fertilizers on plant growth, highlighting both their advantages and disadvantages.
Understanding chemical fertilizers
- Chemical fertilizers are synthetic compounds that contain nutrients essential for plant growth, such as nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and potassium (K).
- These nutrients are essential for the growth and development of plants, influencing processes such as photosynthesis, root formation and flowering.
- They are typically manufactured using industrial processes and are tailored to specific soil types and crops.
Impacts of chemical fertilizers on plant growth.
- Chemical fertilizers improve plant growth and development by making nutrients readily available.
- Nitrogen Fertilizers improve the growth and vigor of plants, especially leafy green vegetables.
- Nitrogen, For example, it is necessary for the formation of proteins, enzymes and chlorophyll, which are essential components of plant cells.
- Match promotes root development and flowering, while potassium improves disease resistance and plant health and helps them resist environmental stress.
Phosphorus Cycle: Introduction, Steps, Importance, Human Impacts (thesciencenotes.com)
- When used correctly, chemical fertilizers can promote plant growth and crop quality. However, excessive or inappropriate use can have a negative impact on plants and ecosystems.
Negative effect of chemical fertilizers on plants.
- Nutrient imbalance: Excessive use of chemical fertilizers can alter the balance of nutrients in the soil, causing deficiencies or toxicities in plants. For example, unnecessary application of nitrogen can promote rapid vegetative growth while inhibiting flowering and fruiting, reducing crop yield and quality.
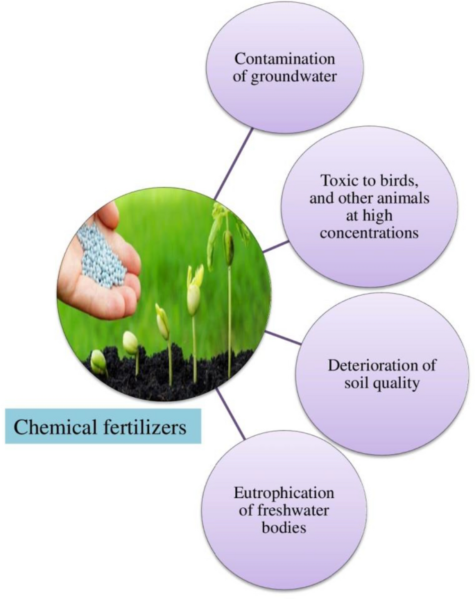
- Soil degradation
- Prolonged use of chemical fertilizers can lead to soil degradation and nutrient depletion.
- Overreliance on specific nutrients can cause imbalances in soil pH, resulting in acidification or alkalization.
- Chemical fertilizers can alter soil microbial communities, resulting in reduced fertility over time.
- Reduced nutrient absorption: Plants grown in soils with high levels of chemical fertilizers can become dependent on external inputs, reducing nutrient uptake capacity. This dependence can reduce the natural resilience of plants, making them more vulnerable to pests, diseases, and environmental stressors.
- Environmental pollution: Runoff from chemically fertilized fields can contaminate water bodies, causing eutrophication and harmful algal blooms. Nitrogen and phosphorus runoff can also lead to groundwater contamination, endangering human health and aquatic ecosystems.
- Plant physiology: Prolonged exposure to high concentrations of chemical fertilizers can alter the physiology and metabolism of plants, affecting photosynthesis, respiration and hormonal regulation. These disruptions can stunt plant growth and reduce overall productivity.
Mitigation strategies and sustainable alternatives
To reduce the negative effects of chemical fertilizers on plants and ecosystems, several mitigation strategies and sustainable alternatives can be implemented:
- Precision farming: Techniques such as soil testing, nutrient management planning, and selective fertilizer application can improve nutrient efficiency and reduce fertilizer waste..
- Organic and natural fertilizers: Using organic and natural fertilizers such as compost, manure and biofertilizers can improve soil health, increase microbial diversity and provide plants with a more balanced nutrient supply.
- Crop Rotation and Cover Crops: Adding cover crops to cropping systems can improve soil structure, nutrient cycling and pest management, reducing the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
- Integrated Nutrient Management: Combining different nutrient sources, such as chemical fertilizers, organic amendments and microbial inoculants, can result in a more sustainable and resilient agricultural system while reducing environmental impact..
- Nutrient recycling: Practices such as crop residue management, nutrient recovery from waste streams, and precision irrigation can improve nutrient efficiency while reducing the need for external inputs.
Regulations and policy
- Chemical fertilizers are regulated globally by governments to protect both the environment and human health.
- Nutrient management plans and best practices optimize fertilizer use and minimize environmental impact.
- Research and development efforts aim to create environmentally friendly fertilizers, including slow-release formulations and nutrient-efficient crops.
- Without a doubt, chemical fertilizers have helped boost agricultural productivity and food security around the world. However, indiscriminate use endangers plant health, soil fertility and environmental sustainability.
- By implementing integrated nutrient management practices and adopting sustainable alternatives, we can reduce the negative effects of chemical fertilizers while promoting healthy plant growth and ecosystem resilience.
- Balancing the benefits of chemical fertilizers with their potential drawbacks is critical for long-term agricultural sustainability and protecting the health of our planet.
Learn more about the
Phosphorus Cycle: Introduction, Steps, Importance, Human Impacts (thesciencenotes.com)
Nitrogen Cycle: Introduction, Steps and Importance (thesciencenotes.com)











Leave feedback about this