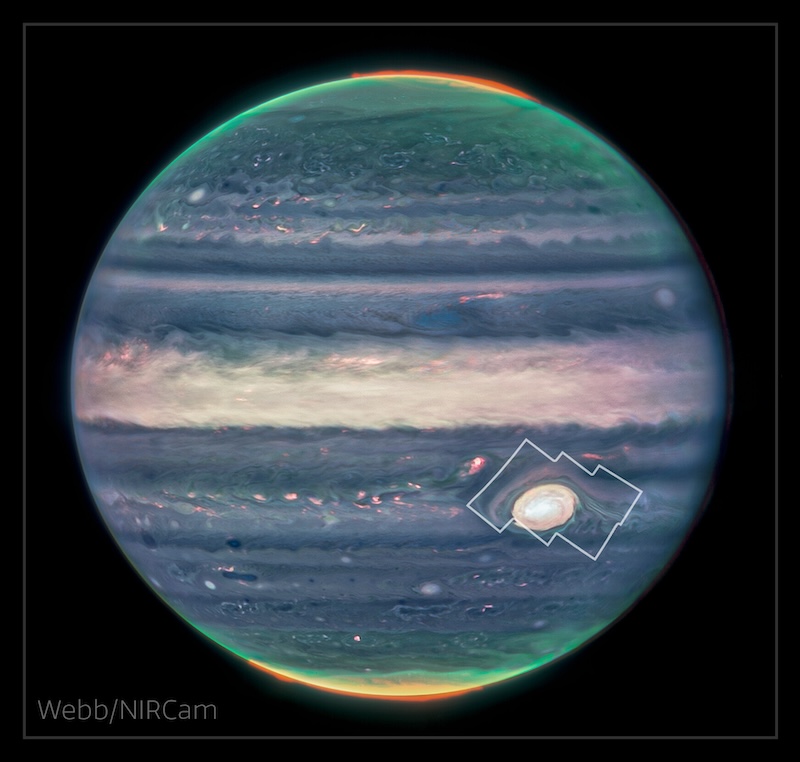
- The atmosphere above Jupiter's Great Red Spot It is active and dynamic, according to astronomers observing it with the James Webb Space Telescope, who expected it to be calmer.
- Webb found a surprising amount of activityincluding dark arcs and bright spots throughout the telescope's field of view.
- Gravity waves in the atmosphere may be creating an unexpected amount of complexity in the region above the Great Red Spot.
Jupiter's Great Red Spot hides surprises
Jupiter's Great Red Spot is a 190-year storm larger than Earth. However, scientists thought that the atmosphere above The storm was fairly benign and uneventful. But on June 24, 2025, astronomers saying They used NASA James Webb Space Telescope Discovering the region is not as simple as expected. In fact, they found a variety of atmospheric shapes and structures never seen before.
The international team of researchers published his peer reviewed findings in Astronomy of nature June 21, 2024.
Observing the region above Jupiter's Great Red Spot
The Great Red Spot is a massive storm on Jupiter that spins counterclockwise. It's a turbulent and chaotic place, to be sure. But scientists thought that the upper atmosphere just above the spot was much calmer, almost dull, even. They thought that the atmosphere in this region would be more homogeneous, due to the fact that Jupiter receives only 4% of the sunlight that Earth does. Therefore, the influence of sunlight on the atmosphere should be much smaller.
However, there are some bright spots Auroras at Jupiter's polesThese auroras are the result of volcanic material from Jupiter's moon. I hitting the planet's magnetic field just above the upper atmosphere.
The researchers wanted to take a closer look at the region just above the Great Red Spot. To do so, they used the Near Infrared Spectrograph (NIR specific) at Webb for observations in July 2022. The research team focused on the atmosphere above the Great Red Spot.
Did you know that Jupiter's Great Red Spot is shrinking?
An astonishing array of intricate structures
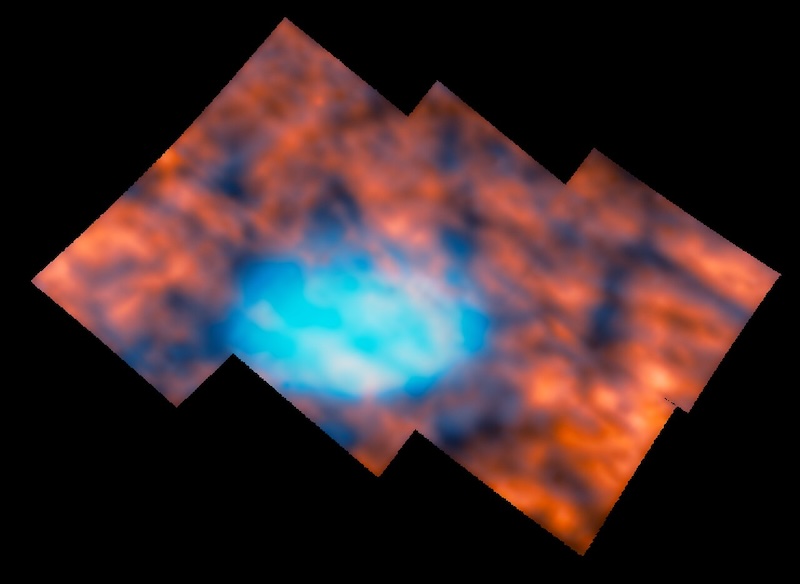
To his surprise, this region turned out to be much more active than expected. Webb revealed dark arcs and bright spots across the field of view. Lead author Henrik Melin at the University of Leicester in the United Kingdom saying:
We thought, perhaps naively, that this region would be really boring. In fact, it is just as interesting as the Northern Lights, if not more so. Jupiter never ceases to amaze.
Like paper fixed:
In this paper, we present James Webb Space Telescope H3+ observations of Jupiter's low-latitude ionosphere in the Great Red Spot region, which show unexpected small-scale intensity features such as arcs, bands, and spots. Our observations may indicate that Jupiter's low-latitude ionosphere is strongly coupled to the lower atmosphere through superimposing gravity waves to produce this complex and intricate morphology.
Why is this region above the Great Red Spot so active?
The researchers said sunlight alone cannot explain why the atmosphere above the Great Red Spot is much more active than previously thought. One answer could be gravitational waves. Melin explained:
One way to change this structure is through gravitational waves, similar to waves crashing on a beach and creating ripples in the sand. These waves are generated deep in the turbulent lower atmosphere around the Great Red Spot and can travel to high altitudes, changing the structure and emissions of the upper atmosphere.
Researchers plan to conduct more follow-up observations to see how the arcs and spots move and change over time. You can watch similar waves They sometimes occur in Earth's atmosphere, but are much weaker than those possible on Jupiter.
Just a few days ago, another group of astronomers also said that the Great Red Spot is probably only about 1,000 years old. 190 years in its present form. Therefore, it is not the same storm that astronomers first saw in the 17th century.
Juice Mission
In July 2031, ESA's Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer probe (Juice) will reach Jupiter. Juice will study Jupiter and three of its largest moons: Ganymede, Calisto and Europe – in incredible detail. You will be able to observe the Great Red Spot and the atmosphere up close.
Bottom line: The Webb Space Telescope observed Jupiter's Great Red Spot and found that the atmosphere above it is much more active and dynamic than astronomers expected.
Source: Ionospheric irregularities on Jupiter observed by JWST
Read more: Jupiter's Great Red Spot is 190 years old, scientists say
Read more: Jupiter's Great Red Spot is shrinking! See photos













Leave feedback about this