
The North Star, also known as Polaris
The North Star, also known as polar Star, appears to remain fixed in our northern sky. Mark the location of the north pole of the sky, or the north celestial pole, the point around which the entire star-filled northern sky revolves. That's why you can always use Polaris to find the north direction.
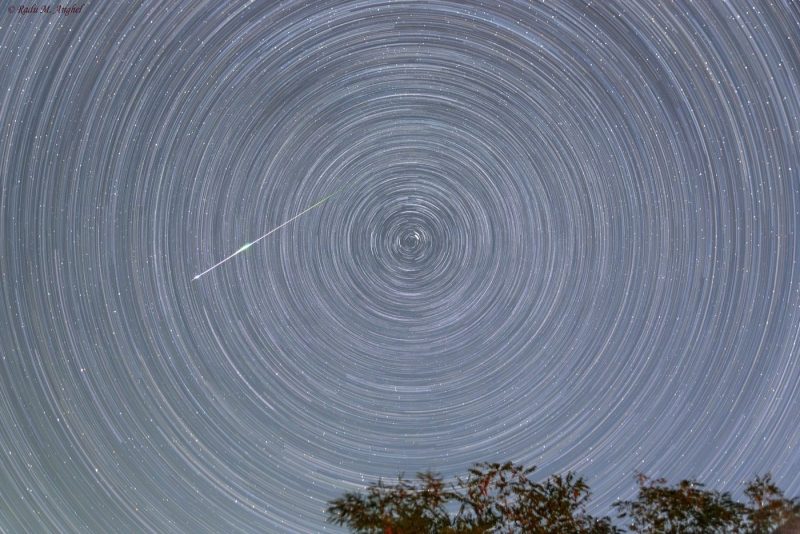
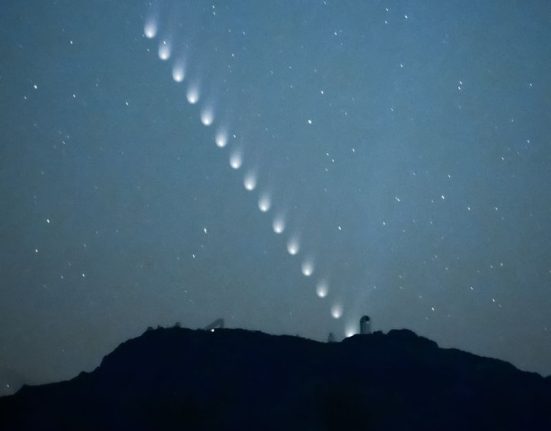
Although the North Star does not seem to move, it does does move. The North Star is a symbol of perseverance. But an overnight video reveals that it makes its own small circle around the north pole of the sky every day. This is because the North Star is slightly displaced (approximately 0.65 degrees – of the celestial north. So, Polaris forms a circle 1.3 degrees in diameter each day. When it is closest to the celestial pole in about 100 years, at a distance of just 0.45 degrees, it will make a daily circle of just 0.90 degrees.
Where does this movement (or in the case of Polaris, the lack of movement) come from? It comes from the Earth's spin. The Earth spins under the sky once a day, and our spin causes the sun during the day (and the stars at night) to rise in the east and set in the west. But the North Star is a special case. Because it lies almost exactly above the Earth's northern axis, it is like the center of a wheel. It doesn't rise or fall. Instead, it appears to stay still in the northern sky.

How high in your sky?
Not only does the North Star point north, but its height in the northern sky also matches your latitude on earth. If you sail through the Caribbean at 16° north latitude, North Star will be about 16° high in your sky. If you sail around Nova Scotia, at 44° north latitude, then the North Star will be about 44° high in the northern sky. Each degree north or south is equal to 69 miles (111 km), so traveling 690 miles north or south will change your latitude and the elevation of the North Star by 10 degrees.
Read more: Polaris is the North Star
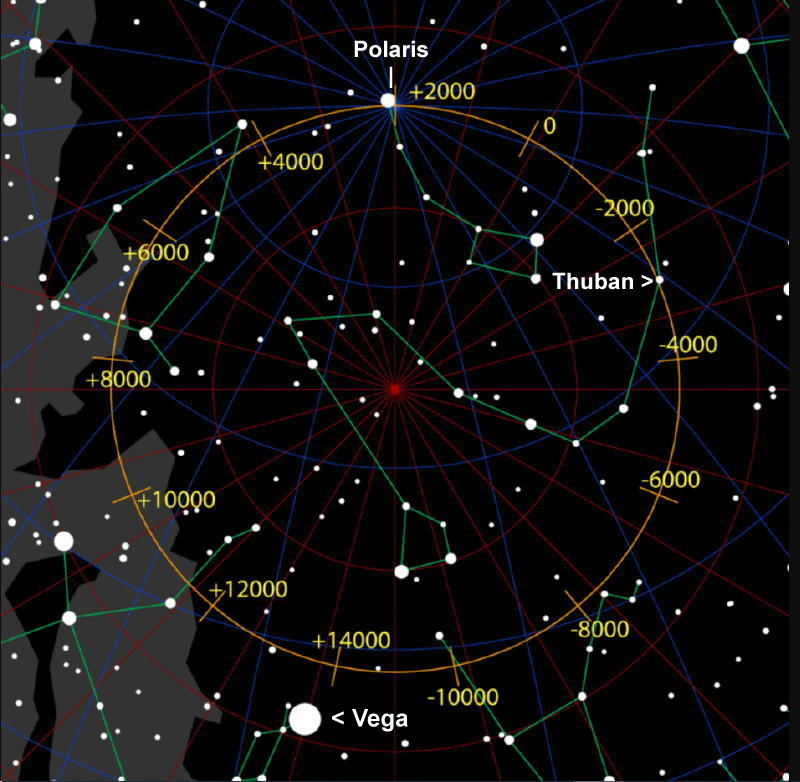
Taking turns as the North Star
A movement of the Earth called precession It makes our axis trace an imaginary circle on the celestial sphere every 26,000 years. Thousands of years ago, when the pyramids rising from the sands of ancient Egypt, the North Star was a discrete star called Thuban in the constellation Draco the Dragon. Twelve thousand years from now, the blue-white star Vega In the constellation Lyra, the Harp will be a pole star much brighter than our current Polaris.
Polaris could be a name for any North Star. Our current Polaris used to be called Phoenice. It is the 49th brightest star in the sky. It is not known for its brightness, but for its unique position in the sky.
proper movement
By the way, Polaris, like all stars, has more than one type of movement. The stars we see in our night sky are all members of our Milky Way galaxy. All of these stars move through space, but they are so far away that we can't easily see them move relative to each other. That's why the stars seem fixed to each other. And that's why, for the most part, we see the same constellations as our ancestors.
But over time, this movement, called proper movement Rearranges the star patterns we see in our sky. For Polaris, that movement is small, approximately 46 seconds of arc in 1,000 years. This is approximately 1/40 of the diameter of the full moon as seen from the ground. So when you talk about stars Moving or stay fixed, remember… everyone is moving through the vastness of space. It is simply the relatively short time of the human life that prevents us from seeing this great movement.
Enjoying EarthSky? Subscribe to our free daily newsletter today!
Simply put: the North Star is a symbol of perseverance. But an overnight video reveals that it makes its own small circle around the north pole of the sky every day.













Leave feedback about this