A comet explosion nearly killed humanity 12,800 years ago
About 12,800 years ago, a geological blink of an eye, global temperatures plummeted suddenly and dramatically. The frigid conditions of the Younger Dryas cooling period lasted more than 1,200 years. But it shouldn't have happened. The Earth was warming when the cooling began. On June 25, 2024, scientists saying More evidence has been found that a comet impact could have been responsible for Earth's sudden cooling.
The researchers published his peer reviewed Article from May 8, 2024 in the journal ScienceOpen Airbursts and crater-forming impactsThey said physical evidence shows a 62-mile-wide (100 km) comet exploded around the same time humanity invented agriculture.
Previously published studies show that human populations fell dramatically at the same time. The result traffic jam It nearly wiped out the human race. It took us more than three centuries to begin our recovery.

Exotic materials and microscopic metals litter the Earth
Since the hypothetical comet never hit Earth, evidence for its existence comes from a large number of tiny particles in the geological record. These microscopic-sized fragments of material (the metals iridium and platinum, magnetic microspheres, molten glass and tiny nanodiamonds – cover the entire globe. Scientists have found these particles in the sediment layer that coincides with the beginning of the Younger Dryas.
Emeritus Professor James Kennett from the Department of Earth Sciences at the University of California, Santa Barbara saying The team found strong evidence supporting a cometary airburst:
There is a wide range of shocked quartz, so we need to show that they are important for interpreting the cosmic impact, even if they do not reflect a traditional major cratering event. These are very low-altitude “landing” airbursts, almost certainly associated with a comet impact.
Kennett is one of the authors of the new paper. The latest publication is part of a series of academic papers providing increasing evidence for the existence of a cosmic impactor. He altered the destiny of humanityKennett's research even suggests a comet impact. brought about a widespread adoption of agriculture.
The comet explosion occurred from a comet at least 60 miles wide.
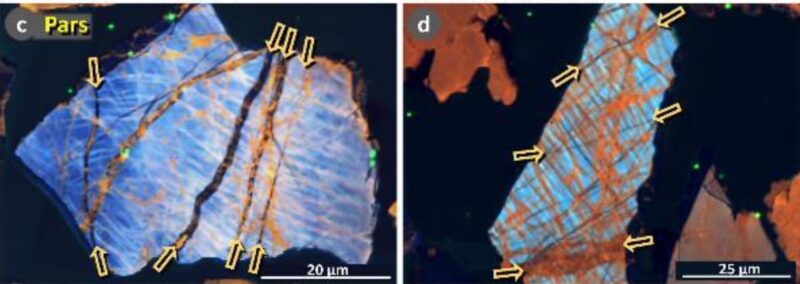
Although there is evidence of radiation from the comet's atmospheric explosion all over Earth (including in Australia), the latest paper focuses on three locations in the eastern United States. All of them are on the East Coast: Flamingo Bay, South Carolina; Parsons Island, Maryland; and Newtonville, New Jersey. A distance of 620 miles (1,000 km) separates the study sites.
Of particular interest to researchers are: sheetstiny laminated layers of alternating materials on microscopic-sized particles. Their abundance in the geologic record 12,800 years ago provides strong evidence of a Younger Dryas comet impact. Kennett explained their significance:
In extreme cases, such as when an asteroid hits the Earth's surface, all the fractures are very parallel. If you think about it, the pressures and temperatures that produce these fractures vary depending on the density, angle of entry, altitude of the impact, and the size of the impacting object.
With this in mind, the evidence suggests that the Younger Dryas comet was about 100 kilometers wide, much larger than the object that killed the dinosaurs. Chicxulub impactor The asteroid that wiped out much of life on Earth is suspected to have been a asteroid. The asteroid that wiped out the dinosaurs was only 10 kilometers in diameter, but because it was much denser and hit Earth, it was much more destructive.
The outburst of the Younger Dryas comet was more like the atmospheric explosion of a meteorite on Tunguska in Russia in 1908. That object was probably only 40 meters wide, but it destroyed 2,150 square kilometers of forest and left no craters.
He Younger Dryas impact hypothesis It remains controversial. There have been repeated attempts to refute the conclusion. However, physical evidence supporting the idea continues to accumulate. In this video, The boys of prehistory Present the history of the evidence – and objections to it – that a comet impact coincided with the onset of the Younger Dryas.
The extinction of megafauna and the loss of the Clovis culture
The Younger Dryas comet did not fall in one piece. Researchers believe it fragmented before exploding. The multiple explosions are responsible for the worldwide distribution of microscopic particles left behind by the disastrous collision. It changed the world forever; the research team wrote:
The consequences of this event, including potential global effects on environmental ecosystems, glacial ice sheets, megafaunal extinctions, and human populations, are not yet fully understood but need to be assessed in the context of a geologically instantaneous and likely catastrophic event.
The airburst could also be the event that sealed the fate of North America. Clovis culturePractitioners of this toolmaking tradition created unique shapes for their weapons. Investigation Other scholars show a 52% decline in Clovis spear points at the same time the supposed cosmic visitor arrived.
Of the world megafauna They were already dying about 40,000 years before the Younger Dryas began. However, there are evidence In the fossil record the extinction process accelerated at that time.
However, not all scientists accept the Younger Dryas impact hypothesis as the cause of the cooling. Others believe the jet stream shifted, causing polar ice to melt. And there is evidence of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (I LOVE C) – which is currently located At its weakest point in 1,000 years – failed completely.
AMOC can be again At the edge of collapse.
Bottom line: New evidence suggests that 12,800 years ago a celestial body exploded in Earth's atmosphere. The catastrophic comet explosion could have cooled Earth's climate for about 1,200 years.
By the University of California, Santa Barbara
Read more: Best photos of comet C/2014 Q1 (PANSTARRS) from ECP contributor Yuri Beletsky
Read more: The extinction of giant herbivores changed global landscapes













Leave feedback about this